vSphere 7 01 Networking
03 Jun 2022
Resources:
Virtual Networking
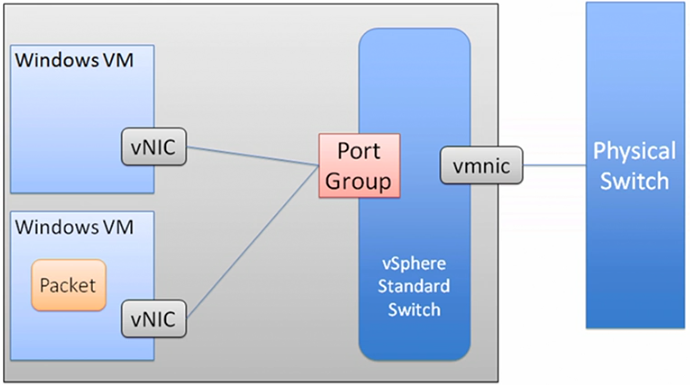
Virtual Machines (VM) are provided with a vNIC (virtual network interface card), from the perspective of the VM operating system this is a normal interface.
The vNICs are connected to a vSwitch (virtual switch) and are assigned a Port Group, which is used to assign:
- VLAN membership
- Security policies
- …
vmNIC, is a physical adaptor, which is used to grant VM access to the external network. These can be considered as up-link ports.
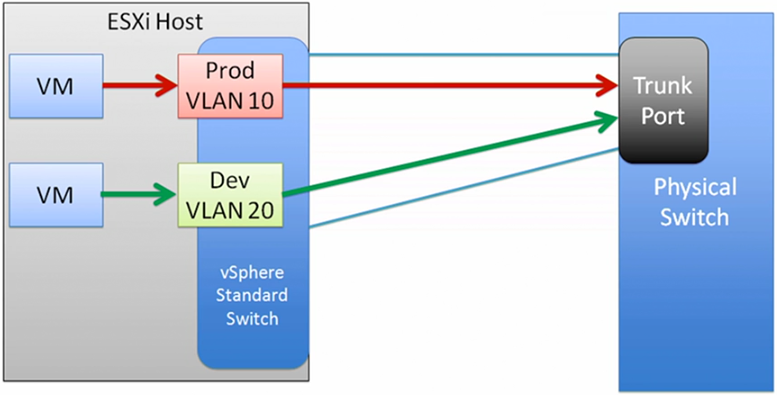
When two different VLANs (virtual local area network) are configured using port groups, the traffic will flow out to a physical switch, to a Trunk port then back in again.
A trunk port is a type of port on a network switch that allows data to flow for multiple VLANs.
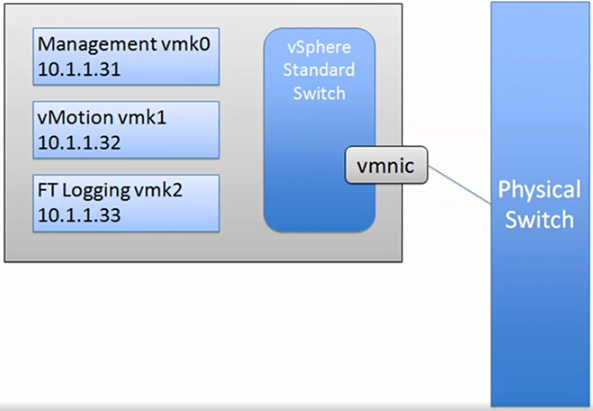
Port Groups are for VM traffic, all other types of traffic are handled using a VMkernel port.
VMkernel ports are specific types of ports that are used for VMware hosts to communicate between one another, such as:
- vMotion
- IP Storage
- Management
Standard Switches
Link Status detects for lost connections on the physical interface, for example the cable has been disconnected.
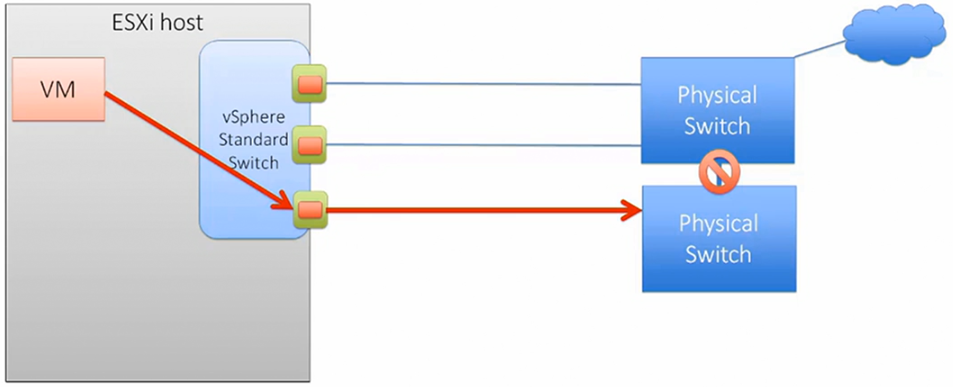
Beacon probes are health packets that are sent between vmNICs to validate they are operational. This solution works best with an odd number of interfaces.
In the figure below the current VM traffic is flowing into an isolated physical switch. In this situation the beacon probes would detect this isolation and redirect the VM traffic.
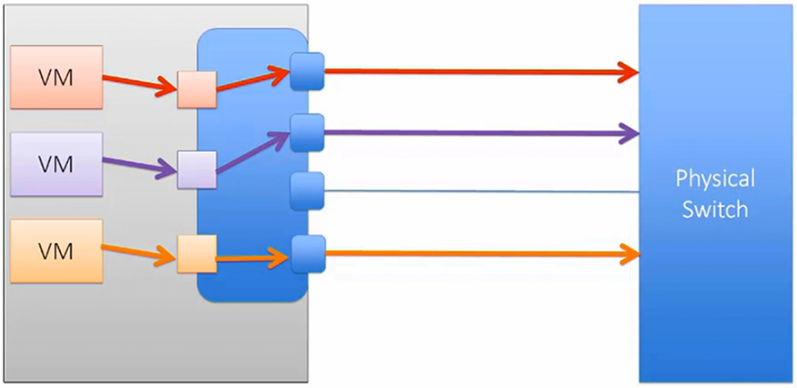
NIC Teaming by Originating Port ID provides a load balance on the vSwitch by directing a specific VM through a specific vSwitch port.
It is important that the physical switch is not configured with any interface teaming such as Etherchannel, Port Channel or LACP.
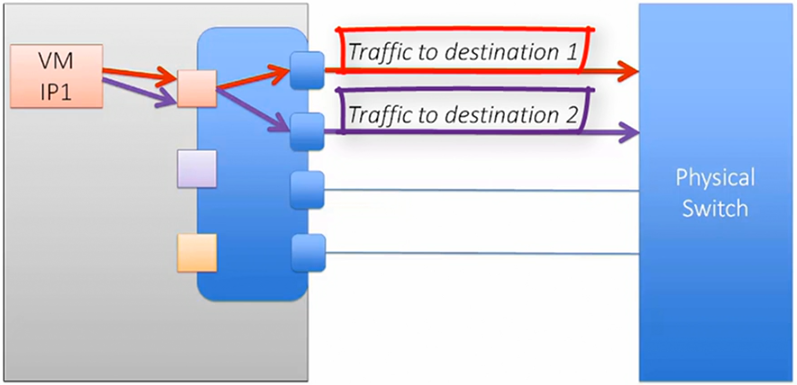
NIC Teaming by Source MAC Hash is very similar to Originating Port ID, but uses the VM MAC (media access control) address.
NIC Teaming by IP Hash, this method uses the source and destination IP addresses to determine which interface traffic should be directed through.
A benefit of this method is that a VM can utilise multiple vmNICs. This means that the physical switch must be configured with Port Channel or LACP to bond the ports.
Egress Traffic shaping is supported with a standard switch and can be assigned to a port group. The following can be configured:
- Peak Bandwidth - VM can peak until the burst size is consumed.
- Average Bandwidth - using under the average builds burst size.
- Burst Size
Security Settings can be configured at the vSwitch or Port Group levels. Any changes at the Port Group level will override the vSwitch level.
Two settings that can be configured are:
- Forged Transmits - Allows MAC spoofing for outbound traffic.
- MAC Address Changes - Allows MAC spoofing for inbound traffic.
- Promiscuous Mode - Allows sniffing of all traffic on the virtual switch.
By default MAC spoofing is configured to “accept” traffic, although for added security it is recommended to configured this to “reject” at the vSwitch level.
Promiscuous mode, is not recommended to leave enabled for security reasons. It should only be enabled for troubleshooting, for example monitoring all traffic on a vSwitch or a system such as IPS/IDS.
vSphere 6 introduced Multiple TCP/IP Stacks, a stack consists of a DNS and Default Gateway. The default stack is used for management, and all other types of traffic.
Although additional stacks can be added for example configuring a different DNS or Gateway for vMotion, this can be useful for long distance vMotion, this can also be used for cold migration, Cloning and Snapshots.
vSphere Distributed Switch
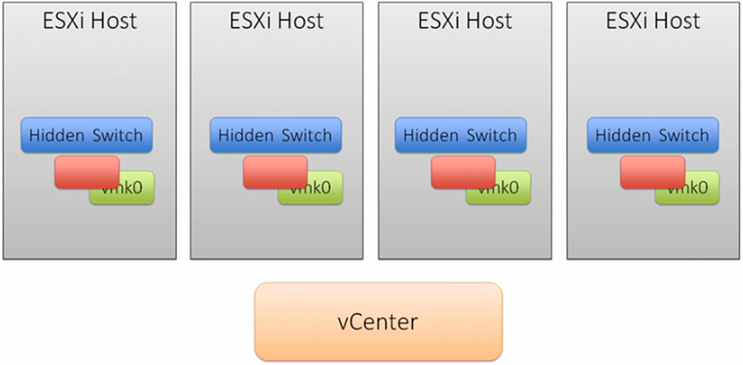
The primary benefit of a vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) is scalability, but is only available with the Enterprise Plus licence.
A distributed switch automates and centralises switch configuration for ESXi hosts, this configured is stored in vCenter. vCenter is the management plane, no traffic flows through it.
VMkernel ports are still configured per ESXi host, as these are the physical interfaces.
Additional features of a distributed switch include:
- LLDP - open standard link layer discovery protocol. CDP is available on both distributed and standard switches.
- Private VLANs - used to isolate traffic within a VLAN, using either Isolated, Community or Promiscuous secondary VLANs.
- Route Based on Physical NIC Load (Load Based Teaming) - Physical interfaces are monitored and when 75% utilisation is reached VMs are migrated to other physical interfaces. Teaming must not be configured on the Physical Switch.
- LACP - open standard for teaming, uses Link Aggregation Groups (LAGs) to form grouped grouped switch ports.
- NetFlow - allows sending vSwitch traffic information to a collector for data analysis.
- Port Mirroring - copies data for a specific port to another port.
- Traffic Shaping - both Ingress and Egress, standard switches can only perform egress.
- Health Check - Validates VLAN, MTU, Teaming and Failover are configured on the physical switch. Although from a security standpoint, this option should not be enabled by default or left enabled.
- Network I/O Control - Prioritise specific types of traffic for example vSAN or iSCSI. Network I/O Control provides Quality of Service (QoS). Shares provide a flexible way to allocate resource, followed by Reservations and Limits, which are fairly inflexible.
NSX-T
NSX-T 3.0 is a virtual network systems, devices such as routers, firewalls switches, integrate third-party services and micro-segmentation.
Micro-segmentation allows for firewall rules to be created on a per-VM basis.
A N-VDS can be considered as a module that is installed into a virtual distributed switch (VDS) to add additional functionality such as Layer 2 segments, which are similar to port groups but the difference is that NSX can span other hosts such as; KVM or bare metal.
vDS was introduced with vCenter 7, which improves integration and simpifies migration.