vSphere 7 06 VMs and Hosts
19 Jun 2022
Resources:
Register and Unregister a VM
When removing a VM, there are two options:
- Delete from Disk - Will delete all files associated with the VM
- Remove from Inventory (Unregister) - Dissociate the VM, but leaves the files in place.
To register a VM, navigate to the storage and find the .vmx file, then use the option to “Register VM”.
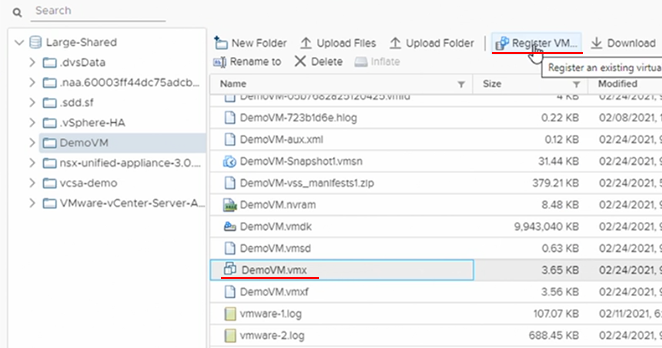
Working with VMX Files
Download a copy of the .VMX file from the datastore.
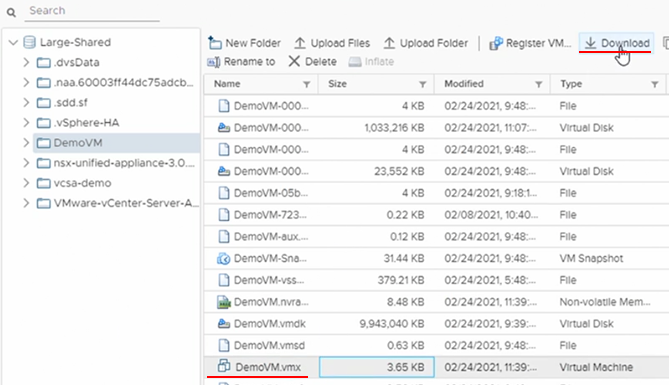
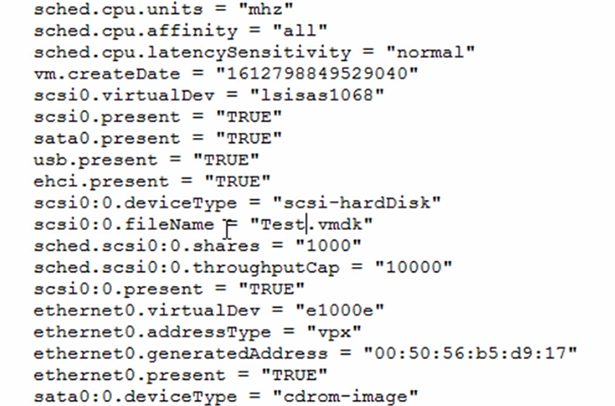
.VMX files are editable via any text editor, as shown below.
Editing the .VMX file in this manner gives the ability to change, for example:
- A corrupt disk
- Network port group
- Snapshot directories
Once the file has been modified, use the “Upload Files” option in the screenshot above.
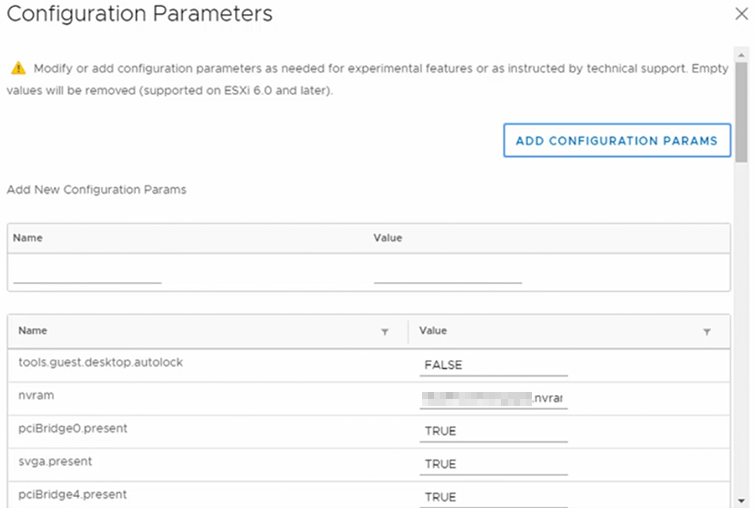
VM Advanced Settings
VM Advanced settings or Configuration Parameters can be found within the VM settings > VM Options > Advanced and click the “Edit Configuration” under Configuration Parameters.
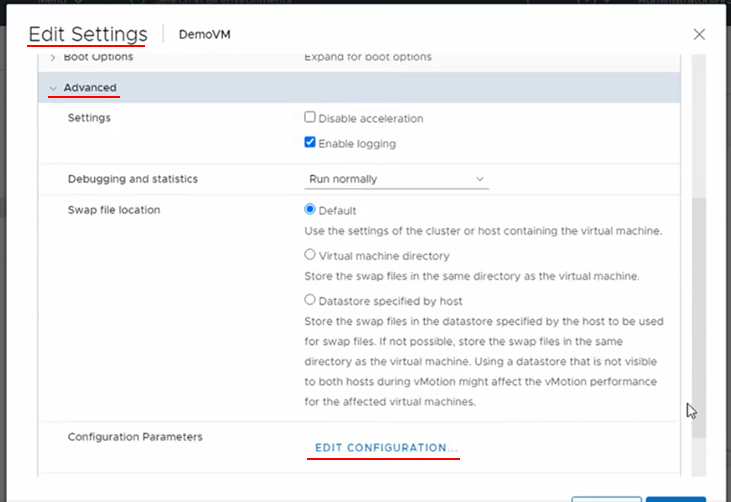
Existing parameters can be modified and additional parameters can be added using the “Add Configuration Params” button.
VMware Docs - Advanced Virtual Machine Attributes
vCenter Converter
In February 2nd, 2022 the vSphere Team removed vCenter Converter as a precautionary measure - Article here.
Possible usages of vCenter Converter are:
- Create a VM based upon a physical server
- Convert another virtual machine format, such as Hyper-V VM into a vSphere VM
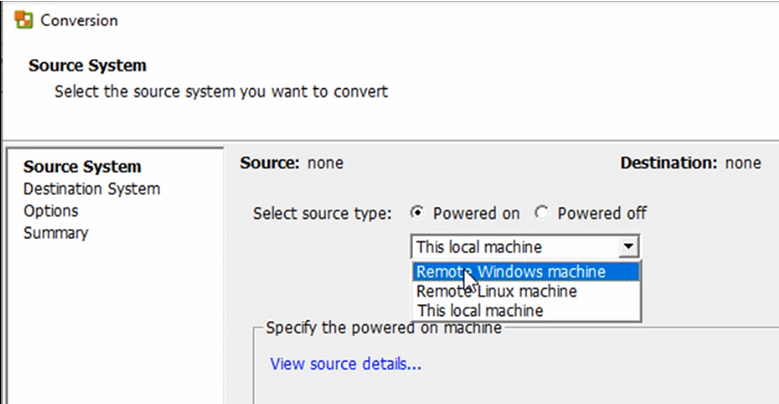
In the Conversion wizard options for the source machine include:
Powered On options:
- Remote Windows machine
- Remote Linux machine
- Local machine - fastest option
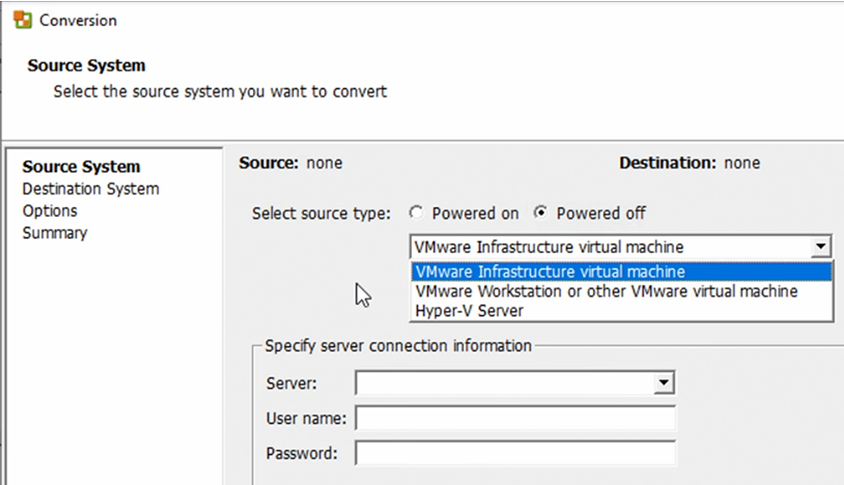
Powered Off options:
- VMware Infrastructure virtual machine
- VMware Workstation or other VMware virtual machine
- Hyper-V Server
VM settings can be modified during conversion, for example disks can be changed from Thick to Thin provision.
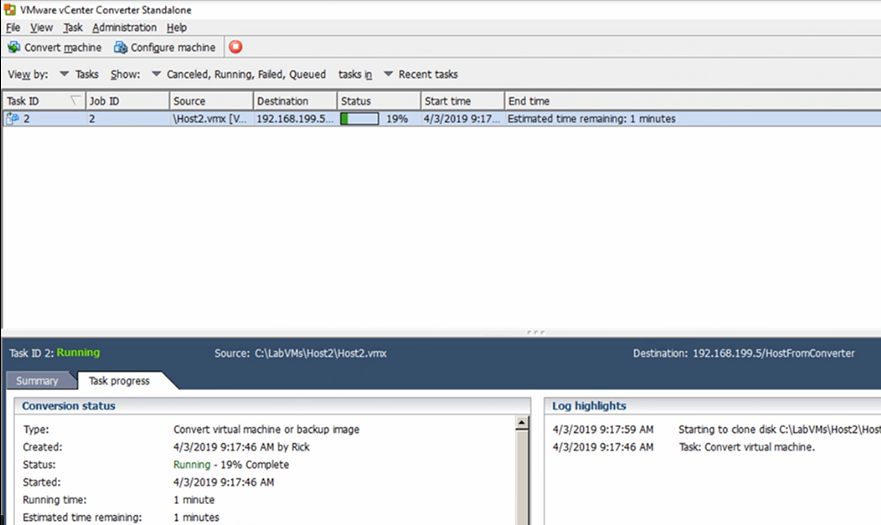
The figure below shows a conversion progress in action.
Assignable Hardware
Modern workloads greatly benefit from using hardware accelerators such as a GPU (Graphical Processing Unit).
Assignable Hardware provides a level of abstraction, that is a flexible mechanism to assign hardware accelerators to workloads.
Assignable Hardware brings back the vSphere HA capabilities to recover workloads (that are hardware accelerator enabled) if assignable devices are available in the cluster.
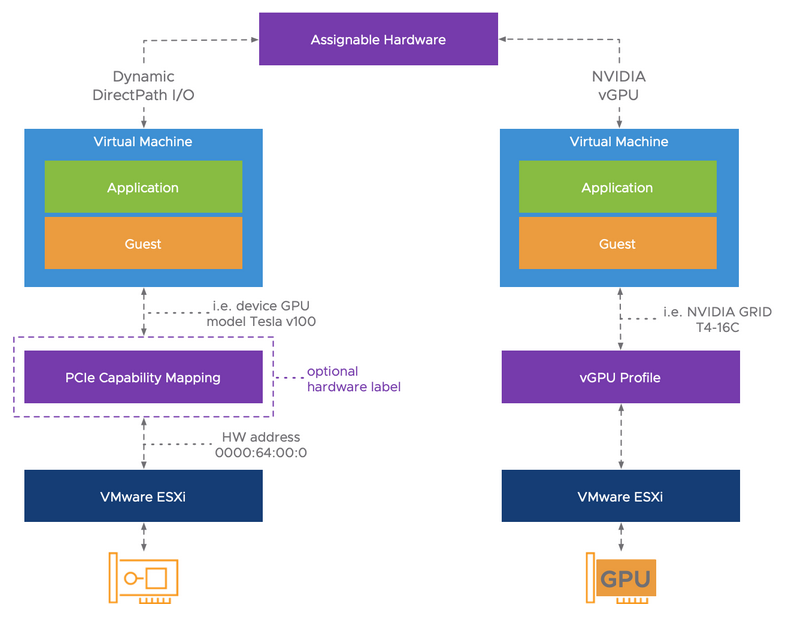
- DirectPath I/O
- Legacy feature to passthrough a PCIe
- Uses hardware addresses, this restricts that virtual machine to that particular host.
- No integration with vSphere DRS and HA
- Dynamic DirectPath I/O
- New solution that enables the Assignable Hardware intelligence for passthrough devices.
- Does not use hardware addresses, instead uses attributes, or capabilities, that are exposed to the virtual machine.
- vSphere HA and DRS (initial placement) capabilities
- NVIDIA vGPU
- Versatile solution that allows for partial, full, or multiple GPU allocation to workloads.
- Allows for workload portability, even live-migrations using vMotion
Auto Deploy
Bare-metal deployment of ESXi hosts using PXE.
- Bare metal boots up and requests an IP address and TFTP address.
- Request a PXE boot file.
- HTTP request to vCenter for an ESXi image, based on the rules engine.
- Boots up as a ESXi host.
- Added to an inventory and applies a host configuration file.
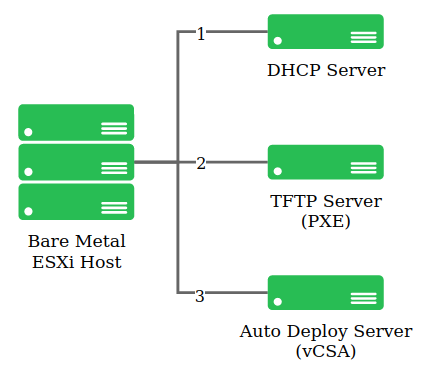
Auto Deploy images are made up of a base VIB and includes other VIBS such as partner solutions and drivers.